The Sovereign SDK Book
The Sovereign SDK is a batteries-included framework for building onchain applications.

Why Rollups?
As a developer, building your application as a rollup has several advantages:
- Dedicated throughput: your users won't pay more just because another app is generating a lot of transactions.
- Scalability: Sovereign SDK nodes scale seamlessly to thousands of transactions per second on commodity hardware, and can achieve substantially higher throughput on optimized hardware.
- Incentive alignment: the vast majority of the rollup fees can be distributed to users and developers of the rollup, rather than subsidizing token holders on L1.
- MEV mitigation: since you have full control over your rollup logic, you can design your protocol to minimize MEV and capture the portions that can't be eliminated.
- Flexibility: rollups enable you to express whatever logic you want, without worrying about the needs of other applications. Enable cutting edge EIPs and account abstraction, or ditch the EVM entirely and build an app-specific chain. With a rollup, you're in the driver's seat.
Why Sovereign?
The Sovereign SDK is the most flexible framework for building rollups. Unlike other rollup frameworks, the Sovereign SDK supports rollups without a settlement layer. That means that you can deploy your rollup anywhere - including on Bitcoin and Celestia. The SDK also provides top-tier scalability and a seamless user experience, all without sacrificing flexibility. Teams are already using the Sovereign SDK to build...
- An EVM chain on Bitcoin
- A MoveVM chain on Celestia
- Appchains on Solana
... and much more.
How it Works
As a developer, you write the business logic of your rollup in Rust and the SDK handles all of the complexity of creating a rollup on their behalf. Under the hood, the SDK compiles the chain's business logic to a zero-knowledge circuit, which it uses to prove correct execution (if the rollup is running in "zk mode") or to resolve disputes about execution (if the rollup is running in "optimistic mode"). It also generates a complete full node implementation which can reproduce the state of the blockchain and serve data to users.
Once the rollup is deployed, users post their transactions onto an underlying blockchain called a Data Availability Layer ("DA Layer") for ordering. After transactions are ordered, the full nodes of the rollup execute them to compute the new rollup state.
Finally, specialized actors called "provers" or "attesters" generate a proof that the new rollup state was computed correctly and post the proof back onto the DA layer. This enables clients of the rollup to verify claims about the rollup state without running a full node for themselves.
Getting Started
TODO. In the meantime, use the sov-rollup-starter repo
Rollup Devs
The chapter will explain the key concepts needed to build your own rollup. It's divided into 3 sections:
- Implementing your Business logic as a
Module - Composing
Modules to build a rollup - Interacting with the chain (CLI, Snap, Rest APIs, RPC, Sequencer)
Implementing a Module
A module is the basic unit of functionality in the Sovereign SDK. A module is a
collection of values stored in state, and an optional call function which
allows users to interact with that state onchain. Modules also provide custom
API support and built-in indexing.
In this section, we'll describe how to implement a module and take full advantage of the Sovereign SDKs builtin functionality.
The Module Struct
A typical module definition looks like this.
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { #[derive(Clone, ModuleInfo, ModuleRestApi)] pub struct Example<S: Spec> { /// The ID of the module. #[id] pub(crate) id: ModuleId, /// A reference to the Bank module, so that we can transfer tokens. #[module] pub(crate) bank: sov_bank::Bank<S>, /// A mapping from addresses to users #[state] pub(crate) users: StateMap<S::Address, User<S>>, } }
There are a few things to notice in this snippet.
Derived Traits
First, we derive the ModuleInfo and ModuleRestApi traits.
You should always derive ModuleInfo on your module, since it does important
work like laying out your state values in the database. If you forget to derive
this trait, the SDK will throw a helpful error.
The ModuleRestApi trait is optional but very useful. It tries to generate
RESTful API endpoints for all of the #[state] items in your module. Each
item's endpoint will have the name
{hostname}/modules/{module-name}/{field-name}/, with all items automatically
converted to kebab-casing. For example, you could query an item from the
known_sequencers state value shown in the snippet above at the path
/modules/sequencer-registry/known-sequencers/{address}.
Note that ModuleRestApi can't always generate endpoints for you. If it can't
figure out how to generate an endpoint for a particular state value, it will
simply skip it by default. (Don't worry, you can always add endpoints manually
if you need to! We'll cover this in the next section.). If you want to override
the default behavior and throw a compiler error if endpoint generation fails,
you can add the #[rest_api(include)] attribute on your state value like this:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { #[derive(Clone, ModuleInfo, ModuleRestApi)] pub struct Example<S: Spec> { // Redundant code elided here... #[rest_api(include)] #[state] pub(crate) users: StateMap<S::Address, User<S>>, } }
See the
documentation
on ModuleRestApi for more details.
The Spec Generic
Next, notice that the module is parameterized by Spec type. This paramter
gives you access to a bunch of handy types and cryptographic traits that are
used on the rollup. These includes the Address type used on the rollup, as
well as information about the underlying DA layer, like its Da::Address type,
BlockHeader type, and more. By being generic over the Spec, you ensure that
you can easily change things like the Address format used by your module later
on.
See the
Spec trait docs
for more details.
#[state], #[module], and #[id] fields
Modules may have as many #[state] and #[module] fields as they wish, but
they must have exactly one #[id]. The ModuleInfo macro will automatically
generate a unique identifier for the module and store it in the id field.
#[module] fields are very straightforward. Adding a dependency on another
module will allow your module to access any of it's public fields and/or public
methods. The only downside is that any users of your module will also have to
include the dependency in their rollup.
#[state] fields are the most interesting. They define the layout of the state
that your module will store. There are three primary kinds of #[state]:
StateValues which store a single item, and StateMaps which store a mapping
from keys to values, and StateVecs which store a series of elements, keyed by
index.
Each kind of state item accepts an optional Codec parameter, which determines
how the state value is encoded and decoded for storage. By default, we use
Borsh for everything, but the SDK also provides a BcsCodec which is
compatible with the widely used serde library. If you want to store a type
from a 3rd-party library in you module, you might need to specify the BcsCodec
like this:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { use some_third_party_crate::SomeType; #[derive(Clone, ModuleInfo, ModuleRestApi)] pub struct MyModule<S: Spec> { // Redundant code elided here... #[state] pub(crate) my_map: StateValue<SomeType, BcsCoded>, } }
Note that this is only necessary if the compiler warns you that the type doesn't
suppor BorshSerialize or BorshDeserialize. If the compiler is happy, you
don't need to override the default.
The last important thing to note about state is that for each kind of item
(Value/Map/Vec), we provide a corresponding AccessoryState{Item} type.
Accessory state looks exactly like regular state, but it's write only during
transaction execution. Items stored in accessory state can be queried via the
API, but they don't have to be replicated by everybody running your rollup since
transactions can't read their contents. This makes accessory state much more
efficient than normal state for indexing and other off-chain tasks.
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { use some_third_party_crate::SomeType; #[derive(Clone, ModuleInfo, ModuleRestApi)] pub struct MyModule<S: Spec> { // Redundant code elided here... /// Stores a record of the purchase history of users that can be queried from the API /// but doesn't exist on-chain. This is much cheaper than maintaining the map on chain. #[state] pub(crate) token_buyers: AccessoryStateMap<S::Address, Vec<Price>>, } }
Module Trait Implementation
Once you've defined your module's state layout, you need a way for users to interact with it.
That's where the Module trait comes in. This trait has two important methods,
genesis and call. You can see a simplified version of the trait below:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { trait Module { /// The configuration needed to initialize the module. type Config; /// A module defined argument to the call method. This is usually an enum, /// with one variant for each action a user might take. type CallMessage: Debug + BorshSerialize + BorshDeserialize + Clone; /// A module defined event resulting from a call method. Events invisible to on-chain /// logic, but they're very useful for indexing. type Event: Debug + BorshSerialize + BorshDeserialize + 'static + core::marker::Send; /// Genesis is called once when a rollup is deployed. /// /// You should use this function to initialize all of your module's `StateValue`s and run any other /// one-time setup. Since this function runs only once, it's perfectly acceptible to do expensive operations /// here. Note that your function should still be deterministic, however. fn genesis( &self, genesis_block_header: &<<Self::Spec as Spec>::Da as DaSpec>::BlockHeader, config: &Self::Config, state: &mut impl GenesisState<Self::Spec>, ) -> Result<(), ModuleError>; /// Call accepts a `CallMessage` and executes it, changing the state of the module and emitting events. fn call(&self, message: Self::CallMessage, context: &Context<Self::Spec>, state: &mut impl TxState<Self::Spec>, ) -> Result<(), ModuleError>; } }
Genesis
As you might expect, the genesis function is called exactly once when the
rollup is initialized. It lets the person deploying your module set any initial
configuration and is responsible for making sure that any state values in your
module are initialized (if necessary). Since genesis is only called once, you
don't need to worry about efficiency. However, you do need to be careful not to
do anything non-determinstic. That means no network requests, and no use of
randomness!
As you can see, the genesis function gets passed a user-defined Config
value. As a module author, you can put anything you want here. Deployers of your
rollup will need to instantiate the config at genesis, and you can use it to do
initialization. If your module doesn't need configuring, you can juse use the
empty type ().
genesis also accepts an argument which implements the GenesisState trait.
This argument allows you to read and write to state values in your module and
its dependencies. A typical genesis config definition and genesis function
looklike this:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { // Adapter from the `SequencerRegistry` module pub struct SequencerConfig<S: Spec> { /// The rollup address of the sequencer. pub seq_rollup_address: S::Address, /// The Data Availability (DA) address of the sequencer. pub seq_da_address: <S::Da as DaSpec>::Address, /// Initial sequencer bond pub seq_bond: u128, } pub(crate) fn genesis( &self, _genesis_rollup_header: &<<S as Spec>::Da as DaSpec>::BlockHeader, config: &SequencerConfig, state: &mut impl GenesisState<S>, ) -> Result<()> { self.register_staker( &config.seq_da_address, Amount::new(config.seq_bond), config.seq_rollup_address.clone(), state, )?; } }
Call
The call function provides the transaction processing logic for your module.
It accepts a structured input from a user and a Context which contains
metadata including the sender address. In response to a call, modules may
update their state as well as emitting Events - structured key-value pairs
which are returned to the user and can be queried over the REST API.
If your call function returns an error, all of its state changes are
automatically reverted and any events are discarded. However, any logs generated
by the transaction will still be visible to the node operator. (More on
logging later.)
You can define the CallMessage accepted by your module to be any type you
wish, but an enum is usually best. Be sure to implement borsh and serde
serialization for your type, as well as schemars::JsonSchema and
sov_modules_macros::UniversalWallet. This will ensure that it's maximally
portable across languages and frontends, making it easy for users to securely
generate, review, sign, and send transactions to your module.
The Bank module provides a very typical example of a call implementation:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { fn call(&self, msg: CallMessage, context: &Context<Self::Spec>, state: &mut impl TxState<S>) -> Result<(), Error> { match msg { call::CallMessage::Transfer { to, coins } => { Ok(self.do_transfer(context.sender(), &to, &coins.token_id, coins.amount, state)?) } // Other variants omitted for brevity } } fn do_transfer(&self, from: S::Address, to: S::Address, token_id: &TokenId, amount: Amount, state: &mut impl StateAccessor) -> anyhow::Result<()> { if from == to || amount == 0{ return Ok(()); } // Use a helper to compute the new `from` balance, throwing an error on insufficient funds let new_from_balance = self.decrease_balance_checked(token_id, from, amount, state)?; // Get the current `to` balance and compute the new one // Note that the `get` function can return an error if the call runs out of gas let current_to_balance = self .balances .get(&(to, token_id), state)? .unwrap_or(Amount::ZERO); let to_balance = current_to_balance.checked_add(amount).with_context(|| { format!( "Account balance overflow for {} when adding {} to current balance {}", to, amount, current_to_balance ) })?; // Update both balances and emit an event, reverting on error. self.balances.set(&(from, token_id), &new_from_balance, state)?; self.balances.set(&(to, token_id), &to_balance, state)?; self.emit_event( state, Event::TokenTransferred { from: sender.as_token_holder().into(), to: to.into(), coins, }, ); Ok(()) } }
Just like Ethereum smart contracts and Solana programs, modules accept
inputs that are pre-validated by the chain. That means your module does not
need to worry about authenticating the transaction. In most cases, you also
don't need to worry about manually metering resource consumption. The SDK will
automatically charge gas for any state accesses and deduct the cost from the
sender's balance. However, if your module does any very heavy computation you
may need to meter that explicitly using the Module::charge_gas function.
Optional Functionality - Hooks
In addition to call modules may optionally implement Hooks. Hooks run at
the begining and end of every rollup block and every transaction. BlockHooks
are great for taking actions that need to happen before or after any
transactions execute in a block - but be careful, no one pays for the
computation done by BlockHooks, so doing any heavy computation can make your
rollup vulnerable to DOS attacks.
TxHooks are useful for checking, or to allow your module to monitor actions
being taken by other modules. Unlike BlockHooks, TxHooks are paid for by the
user who sent each transaction.
The FinalizeHook is great for doing indexing. It can only modify
AccessoryState, which makes it cheap to run but means that the results will
only be visible via the API
Using the hooks is somewhat unusual - most applications only need to modify
their state in response to user actions - but it's a powerful tool in some
cases. See the documentation on
BlockHooks
and
TxHooks
and
`FinalizeHook
more details.
Advanced Functionalty - native only code
In this section, we'll describe more advanced functionality - adding custom APIs, supporting JSON-RPC, and instrumenting your code for debugging and optimization.
Any code that you write following the guide in this section needs to be gated
behind the #[cfg(feature = "native")] flag, which signals to the SDK that the
code is not part of the module's state transition function and is not relevant
to any questions about the rollup's current state. This means that it will be
excluded from zk-proof generation (if the rollup is a zk-rollup) or
challenges (if the rollup is optimistic).
Adding Custom REST APIs
You can easily add custom APIs to your module by implementing the
HasCustomRestApi trait. This trait has two methods - one which actually
implements the routes, and an optional one which provides an OpenApi spec. YOu
can see a good example in the Bank module:
impl<S: Spec> HasCustomRestApi for Bank<S> {
type Spec = S;
fn custom_rest_api(&self, state: ApiState<S>) -> axum::Router<()> {
axum::Router::new()
.route(
"/tokens/:tokenId/total-supply",
get(Self::route_total_supply),
)
.with_state(state.with(self.clone()))
}
fn custom_openapi_spec(&self) -> Option<OpenApi> {
let mut open_api: OpenApi =
serde_yaml::from_str(include_str!("../openapi-v3.yaml")).expect("Invalid OpenAPI spec");
for path_item in open_api.paths.paths.values_mut() {
path_item.extensions = None;
}
Some(open_api)
}
}
async fn route_balance(
state: ApiState<S, Self>,
mut accessor: ApiStateAccessor<S>,
Path((token_id, user_address)): Path<(TokenId, S::Address)>,
) -> ApiResult<Coins> {
let amount = state
.get_balance_of(&user_address, token_id, &mut accessor)
.unwrap_infallible() // State access can't fail because no one has to pay for gas.
.ok_or_else(|| errors::not_found_404("Balance", user_address))?;
Ok(Coins { amount, token_id }.into())
}
REST API methods get access to an ApiStateAccessor. This special struct gives
you access to both normal and Accessory state values. You can freely read and
write to state during your API calls, which makes it easy to reuse code from the
rest of your module. However, it's important to remember API calls do not
durably mutate state. Any state changes are thrown away at the end of the
request.
If you implement a custom REST API, your new routes will be automatically nested
under your module's router. So, in the following example, the
tokens/:tokenId/total-supply function can be found at
/modules/bank/tokens/:tokenId/total-supply. Similarly, your OpenApi spec will
get combined with the auto-generated one automatically.
Note that for for custom REST APIs, you'll need to manually write an OpenApi
specification if you want client support.
Legacy RPC Support
In addition to custom RESTful APIs, the Sovereign SDK lets you create JSON-RPC methods. This is useful to provide API compatibility with existing chains like Ethereum and Solana, but we recommend using REST APIs whenever compatibility isn't a concern.
To implement RPC methods, simply annotate an impl block on your module with
the #[rpc_gen(client, server)] macro, and then write methods which accept an
ApiStateAcessor as their final argument and return an RpcResult. You can see
some examples in the Evm module.
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { #[rpc_gen(client, server)] impl<S: Spec> Evm<S> { /// Handler for `net_version` #[rpc_method(name = "eth_getStorageAt")] pub fn get_storage_at( &self, address: Address, index: U256, state: &mut ApiStateAccessor<S>, ) -> RpcResult<U256> { let storage_slot = self .account_storage .get(&(&address, &index), state) .unwrap_infallible() .unwrap_or_default(); Ok(storage_slot) } } }
Operationalizing
In this section, we'll describe how to reason about and measure your module's performance.
Understanding Performance
State Access
The vast majority of the cost of executing a Sovereign SDK transaction comes
from state accesses. When call item.set(&value), the SDK serializes your value
and stores the bytes in cache. When time you access a value using item.get(),
the SDK deserializes a fresch copy of your value from the bytes held in cache,
falling back to disk if necessary.
Each time you access a value that's not in cache, the SDK has to generate a
merkle proof of the value, which it will consume when it's time to generate a
zero-knowledge proof. Similarly, each time you write a new value, the SDK has to
generate a merkle update proof. This makes reading/writing to a hot value, at
least an order of magnitude cheaper than writing to a cold one (where hot
means that the value has already been accessed in the current block.) So, if you
have state items that are frequently accessed together, it's a good idea to
bundle them into a single StateValue or store them under the same key in a
StateMap.
As a rule of thumb, for each 10% locality, you should be willing to add an extra
200 bytes to your StateValue. In other words, if two values are accessed
together 30% of the time, you should put them together unless either of the
state items is bigger than 600 bytes. (Exception: If two items are always
accessed together, you should always group them together - no questions asked).
Cryptography
The other common source of performance woes is heavy-duty cryptography. If you
need to do any cryptographic operations, check whether the Spec trait provides
a method in its Spec::CryptoSpec that already does what you want. If it does,
use that - the SDK will ensure you get an implementation which is optimized for
the SDK's peculiar requirements. If you need access to more exotic cryptography,
you can use pretty much any existing Rust library - but be aware that the
performance penalty might be severe when it comes time to prove your module's
execution, which could limit your total throughput. If you do need advanced
cryptography, you may need to pick an implementation that's suited to a
particular ZKVM (like SP1 or Risc0) and only use that vm with your module.
Instrumenting Your Module
TODO
- Metrics
- Logging/traces
Gas overview and blessed values
Sovereign's SDK transactions should specify gas parameters in a similar way to
Ethereum. When submitting a transaction, you need to specify a handful of gas
parameters (that are stored in a structure called TxDetails) that depend on
the rollup settings but also on the type of call message to execute. We also
have to make sure that the sender holds enough gas tokens in its bank balance to
make sure that the transaction is not rejected due to insufficient funds.
Finally, sequencers need to stake enough tokens to pay for the transaction
pre-execution checks (like signature verification, deserialization, etc.).
This can be quite overwhelming at first glance, hence we provide here a quick summary of the gas parameters with their respective blessed values (this should be enough to execute most transactions that are not compute/storage intensive),
First, let's look at the gas parameters that are required to submit a
transaction (in the TxDetails structure):
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { use sov_modules_api::Spec; use sov_modules_api::transaction::PriorityFeeBips; /// Contains details related to fees and gas handling. pub struct TxDetails<S: Spec> { /// The maximum priority fee that can be paid for this transaction expressed as a basis point percentage of the gas consumed by the transaction. /// Ie if the transaction has consumed `100` gas tokens, and the priority fee is set to `100_000` (10%), the /// gas tip will be `10` tokens. pub max_priority_fee_bips: PriorityFeeBips, /// The maximum fee that can be paid for this transaction expressed as a the gas token amount pub max_fee: u64, /// The gas limit of the transaction. /// This is an optional field that can be used to provide a limit of the gas usage of the transaction /// across the different gas dimensions. If provided, this quantity will be used along /// with the current gas price (`gas_limit *_scalar gas_price`) to compute the transaction fee and compare it to the `max_fee`. /// If the scalar product of the gas limit and the gas price is greater than the `max_fee`, the transaction will be rejected. /// Then up to `gas_limit *_scalar gas_price` gas tokens can be spent on gas execution in the transaction execution - if the /// transaction spends more than that amount, it will run out of gas and be reverted. pub gas_limit: Option<S::Gas>, /// The ID of the target chain. pub chain_id: u64, } }
- The
max_feeparameter is the maximum amount of gas expressed in gas tokens that can be charged for the transaction execution. - The
max_priority_feeparameter is the maximum percentage (expressed in basis points) of the total gas consumed by the transaction execution that should be paid to reward the sequencer. This parameter can have any value because there is a safety mechanism that prevents the user from paying more than themax_feein total. - The
gas_limitparameter is the maximum amount of gas (expressed in multidimensional gas units) that can be consumed by the transaction execution. This parameter is optional and can be left unspecified. In the future, we will add support for automatically computing this parameter from transaction simulation. - The
user_balanceparameter is the balance of the sender's account (for the gas token) in the rollup's bank. - The
sequencer_balanceparameter is the balance of the sequencer's account (for the gas token) in the rollup's bank. - The
sequencer_stakeparameter is the staked amount of the sequencer in thesequencer_registrymodule.
Blessed gas parameters:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| max_fee | 100_000_000 |
| max_priority_fee | any (50_000 is a reasonable choice) |
| gas_limit | None |
| user_balance | 1_000_000_000 |
| sequencer_balance | 1_000_000_000 |
| sequencer_stake | 100_000_000 |
Note also that:
- The
base_fee_per_gasparameter (whose initial valueINITIAL_GAS_LIMITis set by the rollup in theconstants.toml) roughtly corresponds to the rollup's gas price and is an internal parameter of the rollup. - A batch can consume up to
INITIAL_GAS_LIMITgas units of gas, and the gas target is1/ELASTICITY_MULTIPLIERtimes that value (for each dimension). - The
base_fee_per_gasis dynamically adjusted based on the gas consumption of the batch. The adjustment follows the EIP-1559 which makes it goes down if the batch consumes more gas than the target (and respectively up if the batch consumes less gas than the target).
The gas specification provides a detailed description of the gas mechanisms used within the SDK.
SDK Contributors
This section provides an overview of the Sovereign SDK aimed at core contributors to the framework. It describes the primary components of the SDK at the level of Rust crates.
Transaction Lifecyle Overview
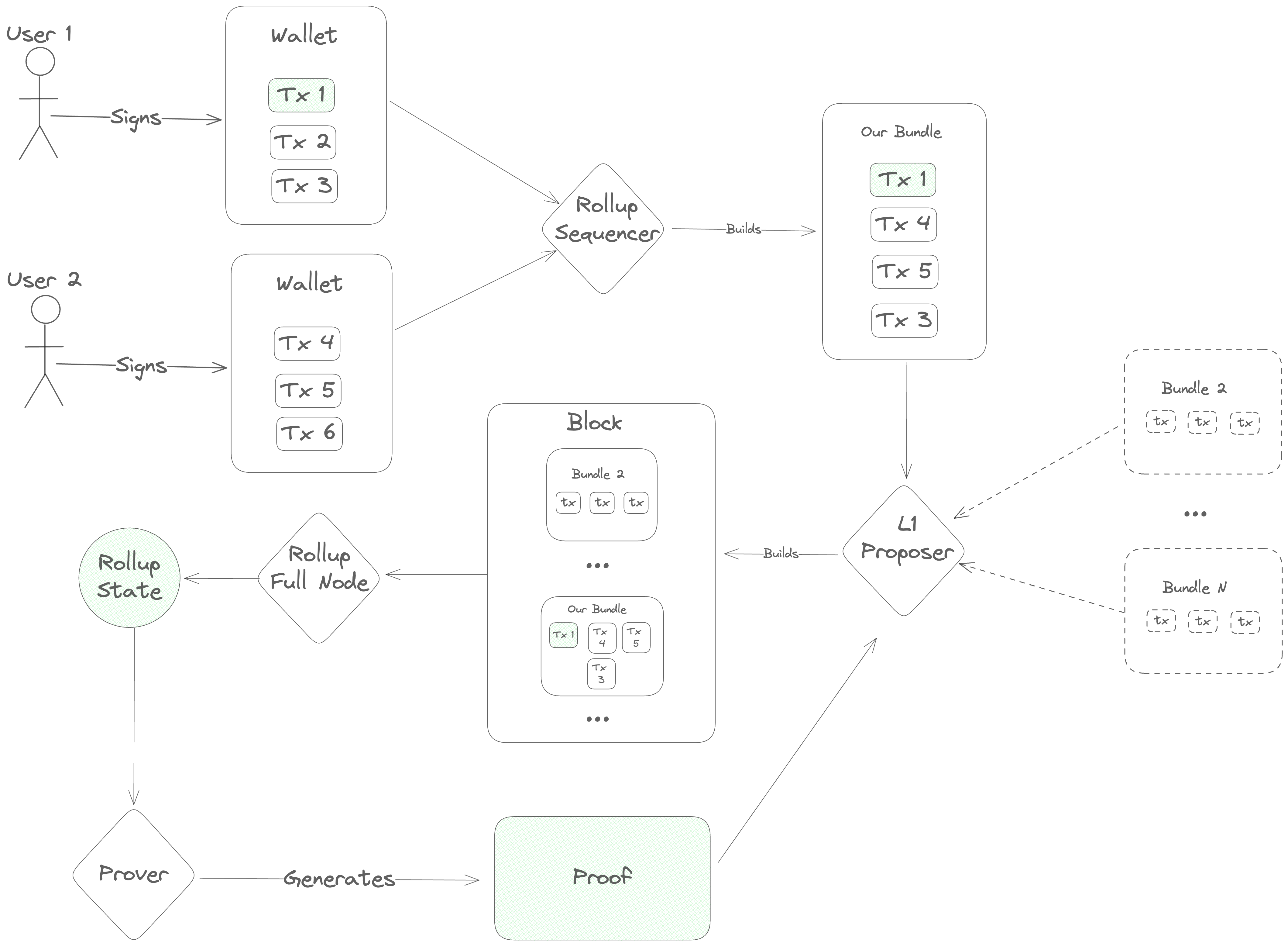
The transaction lifecycle begins with a user. First, the user opens a frontend and gets some information about the current state of the blockchain. Then, they open their wallet and sign a message indicating what action they want to take.
Once a message is signed, it needs to be ordered before full nodes can execute it, so the user's next step is to contact a sequencer to post the transaction onto the DA layer.
The sequencer accepts a number of transactions and bundles them into a single
Blob, which he sends to the DA layer for inclusion. This Blob is
ultimately sent to a Proposer on the DA layer, who includes it in his block
and gets it approved by the DA layer's validator set. Once consensus is reached
on the DA layer block containing the sequencer's Blob, the full nodes of the
rollup parse its contents and execute the transactions, computing a new rollup
state.
Next, specialized actors ("provers" or "attesters") generate a proof of the new
rollup state and post it onto the DA layer. Finally, light clients of the
rollup (end-users and/or bridges on other blockchains) verify the proof and see
the results of the transaction.
SDK Design Philosophy
Now that we've established the basic transaction lifecycle, we have the background we need to really dig into the design of the Sovereign SDK.
At a high level, the design process for the SDK was essentially just tracing the transaction lifecycle diagram and asking two questions at each step:
- "How do we implement this step so that we really 'inherit the security of the L1'?"
- "Within those constraints, how do we build the SDK to accommodate the broadest range of use cases?"
Step 1: Retrieving Information
Before doing anything, users need to find out about the current state of the rollup. How can we enable that?
At this step, we have several conflicting goals and constraints:
- We want the user's view of the rollup to be as up-to-date as possible
- We want to provide the strongest possible guarantees that the user's view of state is correct
- We want to minimize costs for the rollup
- Users may not be willing/able to download more than a few hundred kilobytes of data or do any significant computation
Obviously, it's not possible to optimize all of these constraints simultaneously. So, in the Sovereign SDK, we allow developers some flexibility to pick the appropriate tradeoffs for their rollups - and we give end-users additional flexibility to choose the setup that works best for them.
In practice, that means that...
- Developers can choose between Optimistic and ZK rollups, trading transaction cost for time-to-finality.
- Users can choose between running a full node (instant state access, but expensive), running a light client (slower state access, but much cheaper and trustless) and trusting a full node (instant state access)
Step 2: Signing Transactions
The SDK supports several signing/verification modes. The standard choice for
interacting with Sovereign SDK chains is our custom UniversalWallet, which is
available as a Metamask snap and a Ledger app. The UniversalWallet integrates
tightly with the Sovereign SDK to render transactions in human-readable format.
However, many chains need compatibility with legacy formats like Ethereum RLP
transactions or Solana instructions
We've made the pragmatic choice to be as compatible as possible with existing
crypto wallets using our RuntimeAuthenticator abstraction. By implementing the
RuntimeAuthenticatortrait, developers cab bring their own transaction
deserialization and authorization logic. Even better, we allow rollups to
support several different Authenticator implementations simultaneously. This
allows developers to retain backward compatibility with legacy transaction
formats, without compromising on support for their native functionality.
Step 3: Sequencing
Once a user has signed a transaction, we need to broadcast it to all full nodes of the rollup.
Since a primary design goal is to inherit the security of the underlying blockchain, we want to ensure that users are always able to fall back on the censorship resistance of the L1 if necessary. At the same time, we don't expect users to interact directly with the underlying blockchain in the normal case. The underlying blockchain will charge fees in its own token, and we don't need or want users of the rollup to be thinking about exchange rates and L1 gas limits.
We also need to protect the rollup from spam. In a standard blockchain, spam is handled by ensuring that everyone pays for the computation that the network does on their behalf. Transactions with invalid signatures are filtered out at the peer-to-peer layer and never get included in blocks. This means that an attacker wanting to spam the rollup has no asymmetric advantage. He can send invalid transactions to the few nodes he happens to be directly connected to, but they will just disconnect. The only way to get the entire blockchain network to process a transaction is to provide a valid signature and pay enough gas fees to cover the cost of execution.
In a rollup, things are different. Rollups inherit the consensus of an underlying blockchain which doesn't know about the transaction validity rules of the rollup. Since the underlying chain doesn't know the rules, it can't enforce them. So, we need to be prepared to deal with the fact that the rollup's ledger is dirty. This is bad news, because checking transaction signatures is expensive - especially in zero-knowledge. If we aren't careful, an attacker could flood the rollup's ledger with malformed transactions and force the entire network to pay to check thousands of invalid signatures.
This is where the sequencer comes in. Sequencers accept transactions from users
and bundle them into Blobs, which get posted onto the L1. At the rollup level,
we force all sequencers to register by locking up some tokens - and we ignore
any transactions which aren't posted by a registered sequencer. If a sequencer's
bundle includes any transactions which have invalid signatures, we slash his
deposit and remove him from the registry. This solves two problems at once.
Users don't need to worry about obtaining tokens to pay for inclusion on the
DA layer, and the rollup gets builtin spam protection.
Unfortunately, this setup also gives sequencers a lot of power. Since the sequencer handles transactions before they've gone through the DA layer's consensus mechanism, he can re-order transactions - and potentially even halt the rollup by refusing to publish new transactions.
To mitigate this power, we need to put a couple of safeguards in the protocol.
First, we allow anyone to register as a sequencer depositing tokens into the sequencer registry. This is a significant departure from most existing rollups, which rely on a single trusted sequencer.
Second, we allow sequencers to register without sending a transaction through
an existing sequencer. Specifically, we add a rule that the rollup will
consider up to K extra blobs from unregisterd sequencers in each rollup block.
If any of the first K "unregistered" blobs conform to a special format, then
the rollup will interpret them as requests to register a new sequencer. By
capping the number of unregistered blobs that we look at, we limit the
usefulness of unregistered blobs as a DOS vector while still ensuring that
honest sequencers can register relatively quickly in case of censorship.
Finally, we try to make sequencing competitive by distributing some of the fees from each transaction to the sequencer who included it. This incentivizes new sequencers to register if the quality of service is low.
Ok, that was a lot of information. Let's recap.
In the Sovereign SDK, sequencers are middlemen who post transactions onto the DA layer, but it's the DA layer which ultimately decides on the ordering of transactions. Anyone can register as a sequencer, but sequencers expose themselves to slashing if they include transactions with invalid signatures (or certain other kinds of obvious spam).
That covers a huge chunk of sequencing. But there are still two topics we haven't touched on: stateful validation, and soft confirmations.
Stateful Validation
Up to this point, we've been talking about transactions as if they're always either valid or invalid for all time, regardless of what's happening on the rollup. But in the real world (especially when there are many sequencers), that's not the case. To give just one example, it's entirely possible for an account to burn through all of its funds with a single transaction, leaving nothing to pay gas with the next time around. So, if two sequencers publish blobs at about the same time, it's very possible that the first blob will cause some tranasactions in the second one to become invalid.
This complicates our analysis. Previously, we assumed that a sequencer was malicious if he caused any invalid transactions to be processed. That meant that we could safely slash his deposit and move on whenever we encountered a validation error. But now, we can't make that assumption. Otherwise, sequencers would have to be extremely conservative about which transactions they included - since a malicious (or confused) user could potentially cause a sequencer to get slashed by sending conflicting transactions to two different sequencers at the same time.
On the other hand, we don't want to let sequencers get away with including transactions that they know are invalid. Otherwise, a malicious sequencer could include invalid transactions "for free", causing the rollup to do a bunch of wasted computation.
We address these issues by splitting transasction validation into two categories. Stateless validation (i.e. signature checks) happens first, and transactions which fail stateless validation are invalid forever. If a sequencer includes a transaction which is statelessly invalid, then we know he's malicious. After a transaction has passed stateless validation, we proceed to make some stateful checks (i.e. checking that the transaction isn't a duplicate, and that the account has enough funds to pay for gas). If these checks fail, we charge the sequencer a small fee - just enough to cover the cost of the validatoin.
This ensures that sequencers are incentivized to do their best to filter out invalid transactions, and that the rollup never does any computation without getting paid for it, without being unfairly punitive to sequencers.
Soft Confirmations
Now that we've talked about the minimum requirements for sequencer, we move on to soft-confirmations.
One of the biggest selling points of rollups today is the ability to tell users the outcome of the tranaction instantly. Under the hood, this experience is enabled by giving a single trusted sequencer a "lock" on the rollup state. Because he holds the lock, the sequencer can run a local simulation to determine the exact effect of a transaction before he posts it on the DA layer.
Unfortunately, this introduces a load bearing point of centralization. If the centralized sequencer becomes unavailable (or is malicious), the rollup halts and users have little recourse.
On existing rollups, this issue is somewhat mitigated by providing an "inbox" on the DA layer where users can send special "forced withdrawal" transactions. However, in most existing rollups these "forced" transactions are significantly less powerful than ordinary ones. (Users are often limited to only withdrawing funds) and the delay period before they are processed is long.
In the Sovereign SDK, we try to do better. Unfortunately, there's no way to enable soft confirmations without giving some entity a lock on (some subset of) the rollup state. So, this is exactly what we do. We allow rollup deployers to specify some special "preferred sequencer", which has a partial lock on the rollup state.
In order to protect users in case of a malicious sequencer, though, we make a few additional changes to the rollup.
First, we separate the rollup state into two subsets, "user" space and "kernel" space. The kernel state of the rollup is maintained programatically, and it depends directly on the headers of the latest DA layer blocks. Inside of the protected kernel state, the rollup maintains a list of all the blobs that have appeared on the DA layer, and the block number in which they appeared.
Second, we prevent access to the kernel state of the rollup during transaction execution. This prevents users from creating transactions that could accidentally invalidate soft-confirmations given by the sequencer, as well as preventing the sequencer from deleting forced transactions before they can be processsed.
Finally, we add two new invariants:
-
Every blob which appears on the (canonical) DA chain will be processed within some fixed number of blocks
-
All "forced" (non-preferred) transactions will be processed in the order they appeared on the DA layer
To help enforce these invariants, we add a concept of a "visible" slot number. The visible slot number is a nondecreasing integer which represents block number that the preferred sequencer observed when he started building his current bundle. Any "forced" blobs which appear on the DA layer are processed when the visible slot number advances beyond the number of the real slot in which they appeared.
Inside the rollup, we enforce that...
-
The visible slot number never lags behind the real slot number by more than some constant
Kslots- This ensures that "forced" transactions are always processed in a reasonable time frame
-
The visible slot number increments by at least one every time the preferred sequencer succesfully submits a blob. The sequencer may increment the virtual slot by more than one, but the maximum increment is bounded by a small constant (say, 10).
-
The visible slot number is never greater than the current (real) slot number
-
Transactions may only access information about the DA layer that was known at the time of their virtual slot's creation. Otherwise, users could write transactions whose outcome couldn't be predicted, making it impossible to give out soft confirmations. - For example, a user could say
if current_block_hash % 2 == 1 { do_something() }, which has a different outcome depending on exactly which block it gets included in. Since the rollup sequencer is not the L1 block proposer, he doesn't know what block the transaction will get included in! By limiting transactions to accessing historical information, we avoid this issue.
What all of this means in practice is that...
- The visible state never changes unless either the preferred sequencer submits a batch, or a timeout occurs (i.e. the visible slot lags too far). This ensures that the preferred sequencer always knows the exact state that he's building on top of.
- An honest sequencer wants to keep the virtual slot number as close to the real slot number as possible. This way, he has more buffer to absorb downtime without the state changing. This reduces the risk of soft-confirmations being invalidated.
- Honest sequencers can always give accurate soft confirmations, unless the DA
layer experiences a liveness failure lasting more than
Kslots. - Transactions can access information about the underlying blockchain with the best latency that doesn't invalidate soft confirmations.
Handling Preferred Sequencer Failure
With the current design, the Sovereign SDK supports soft confirmations while providing a reasonably powerful forced transaction mechanism. We also provide some limited protection from a malicious sequencer. If the sequencer is malicious, he can - at worst - delay transaction processing by some constant number of blocks. He can't prevent forced transactions from being processed, and he can't selectively delay transactions.
We also provide some limited protection if the preferred sequencer commits a slashable offense. In this case, the rollup enters "recovery mode", where it reverts to standard "based" sequencing (where all sequencer are equal). In this mode, it advances the virtual slot number two-at-a-time until the rollup is caught up, at which point the rollup behaves as if there had never been a preferred sequencer.
In the future, we may also add slashing if the preferred sequencer gives "soft-confirmations" which turn out to be invalid, but this requires some additional design work.
Step 4: Execution
Once a transaction is sequenced, the rollup needs to process it.
At a high level, a Sovereign SDK transaction goes through the following sequence:
-
(Stateless) Deserialization: Decoding the bytes of the transaction into meaningful components (signature, ChainID, etc)
-
(Stateful) Pre-validation: Checking that the address which is claiming to have authorized the transaction exists and retrieving its preferences for authorization. For example, if the address is a multisig, fetch the set of public keys and the minimum number of signatures.
-
(Usually Stateless) Authentication: Checking that the transaction is authorized. For example, checking that the signatures are valid.
-
(Stateful) Authorization: Matching the results of the authentication and pre-validation steps to decide whether to execute. This step also reserves the funds to pay for gas used during transaction execution. --- State changes up to this point are irreversable. State changes beyond this point are either committed or reverted together
-
(Stateful) Pre-dispatch hook: This hook allows all modules to inspect the transaction (and their own state) and do initialization before the transaction is executed. For example, a wallet module might use this hook to check the user's balance and store it for later retrieval. This hook may abort the transaction and revert any state changes by returning an
Error. -
(Stateful) Execution: The transaction is dispatched to a single target module for execution. That module may invoke other modules if necessary during execution. If this call returns an error, all state changes from step 5 onward are reverted.
-
(Stateful) Post-dispatch hook: This hook allows all modules to inspect their state and revert the transaction if necessary. If this call returns an error, all state changes from step 5 onward are reverted.
-
(Stateful) Post-execution: After transaction execution, any unused gas is refunded to the payer
As described in the "Sequencing" documentation, sequencers are slashed if any of the two stateless steps fail. If either of the stateful steps prior to execution fail, the sequencer is penalized - but just enough to cover the cost of the work that has been done. If the transaction fails during execution, the costs are paid by the user (or whichever entity is sponsoring the gas cost of the transaction.)
For more details on execution, see [TODO]
Step 5: Proving
Once a transaction is executed, all of the rollup full nodes know the result instantly. Light clients, on the other hand need proof. In this section, we'll describe the different kinds of proof that the Sovereign SDK offers.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs
The most powerful configuration for a rollup is zero-knowledge mode. In this mode, light clients can trustlessly sync the chain with near-zero overhead and only minutes of lag behind the chain tip. This enables fast and trustless bridging between rollups, and between the rollup and the execution environment of its DA layer (if applicable).
In the Sovereign SDK, proving is asynchronous (meaning that we post raw transactions on the DA layer - so that full nodes can compute the rollup state even before a proof is generated). This means that light clients have a view of the state that lags a little bit behind full nodes.
Proof Statements
All zero-knowledge proofs have the form, "I know of an input such that...". In our case, the full statement is:
I know of a DA layer block with hash X (where X is a public input to the proof) and a rollup state root Y (where Y is another public input) such that the rollup transitions to state Z (another public input) when you apply its transaction processing rules.
To check this proof, a client of the rollup needs to check that the input block hash X corresponds to the next DA layer block, and that the input state root Y corresponds to the current rollup state. If so, the client can advance its view of the state from Y to Z.
This works great for a single block. But if a client needs to validate the entire history of the rollup, checking proofs of each block would get expensive. To alleviate this problem, we use recursive proofs to compress multiple block proofs into one. (A nice property of zero-knowledge proofs is that the work to verify a proof is roughly constant - so checking this recursive "aggregate" proof is no more expensive than checking the proof of a single block.)
Each AggregateProof is a statement of the form:
I know of a (previous) valid
AggregateProofstarting fromA(the genesis block hash, a public input) with state rootB(the rollup's genesis state, a public input) and ending at block hashCwith state rootD. And, I know of a sequence of valid proofs such that...
- For each proof, the block header has the property that
header.prev_hashis the hash of the previous header- For each proof, the input state root is the output root of the previous root.
- The block header from the first proof has
prev_hash == C- The first proof has has input state root
D- The final proof in the chain has block hash
Aand output rootB(whereAandBare public inputs)
Incentives
Generating zero-knowledge proofs is expensive. So, if we want proofs to be generated, we need to incentivize proof creation in protocol, preferrably using the gas fees that users are already paying.
In a standard blockchain, the goal of transaction fees markets is to maximize consumer surplus. They achieve this by allocating a scarce resource (blockspace) to the people who value it most. Analysis shows that EIP-1559 is extremely good at solving this optimization problem in the setting where supply is fixed and demand varies rapidly. EIP-1559 adjusts the price of blockspace to the exact price level at which demand matches supply.
In zk-rollups, we have a slightly different setup. Our supply of blockspace is not constant. Instead, it's possible to invest more money in proving hardware in order to increase the rollup's throughput. However, bringing more prover capacity online takes time. Deals have to be negotiated, hardware provisioned, etc. So, in the short term, we model prover capacity as being fixed - and we use EIP-1559 to adjust demand to fit that target.
In the long run, we want to adjust the gas limit to reflect the actual capacity of available provers. (Note that this is not yet fully implemented). To facilitate this, we will track the rollup's gas usage and proving throughput (measured in gas per second) over time. If rollup blocks are full and provers are able to keep up, we will gradually increase the gas limit until blocks are no longer full or provers start to fall behind.
This still leaves one problem... how do we incentivize provers to bring more hardware online? After all, adding more hardware increases the gas limit, which increases the supply of blockspace. This causes congestion (and fees) to fall, increasing consumer surplus. But provers don't get paid in consumer surplus, they get paid in fees. So, adding more hardware hurts provers in two ways. It increases their costs, and it reduces the average fee level. This means that provers are incentivized to provide as little capacity as possible.
The way we handle this problem is by introducing competition. In Sovereign, we only reward the first prover to publish a valid proof of a block. Since proving is almost perfectly parallel, and provers are racing to prove the block first, a prover which adds slightly more capacity than its rivals experiences a disproportionate increase in rewards. This should encourage provers to bring as much capacity as possible.
Since we want to reward provers with funds on the rollup, we need consensus.
(Otherwise, it would be trivial to cause a chain split by creating a fork which
sent some rewards to a different prover.) So, we require provers to post their
proofs on chain. The first prover to post a valid proof of a particular block
gets rewarded with the majority of the base_fees collected from that block.
This is a deviation from EIP-1559, where all base fees are burned. Intuitively,
our construction is still safe because provers "burn" money in electricity and
hardware costs in order to create proofs. However, we also burn a small
proportion of base fees as insurance in case proving costs ever fall to
negligble levels.
Once a prover has posted his proof on the DA layer, two things happen. First, full nodes read the proof and, if it's valid reward the prover. If it's invalid, the prover has his deposit slashed. (Just like a misbehaving sequencer. Also like sequencers, data posted by un-bonded entities is ignored.) Second, light clients of the rollup download and verify the proof, learning the state of the rollup. As an implementation detail, we require proofs which get posted on chain to be domain separated, so that light clients can download just the proofs from a rollup without also needing to fetch all of the transaction data.
Summary: The proving workflow
So, putting this all together, the proving workflow looks like this:
-
A DA layer block is produced at height
N. This block contains some rollup transactions. -
Full nodes immediately process the transactions and compute a new state.
-
Provers begin generating a proof of block
N. -
(About 15 minutes later) a prover creates a valid proof of block
N. In the meantime, DA layer blocksN+1throughN+Xhave been produced.a. At this point, full nodes are aware of rollup state
N+X, while light clients are still unaware ofN -
The prover creates a new
AggregateProof, which...a. Proves the validity of the proof of block
Nb. Proves the validity of the previous
AggregateProof(which covered the rollup's history from genesis to blockN-1)c. Optionally proves the validity of proofs of blocks
N+1,N+2, ...,N+X, if such proofs are available. (Note that theAggregateProofmust cover a contiguous range of blocks starting from genesis, but it may cover any number of blocks subject to that constraint.) For concreteness, suppose that in this case the prover includes blocksN+1throughN+5. -
The prover posts the new
AggregateProofonto the DA layer at some height - call itN+30. At this point, full nodes are aware of stateN+30(which includes a reward for the prover), and light clients are aware of stateN+5. At some point in the future, a proof ofN+30will be generated, at which point light clients will become aware of the prover's reward.
Optimistic Proofs
For some rollups, generating a full zero-knowledge proof is too expensive. For these applications, the Sovereign SDK offers Optimistic Mode, which allows developers to trade some light-client latency for lower costs. With a zk-rollup, light clients have a view of the state which lags behind by about 15 minutes (the time it takes to generate a) zero- knowledge proof. However, at the end of those 15 minutes, light clients know the state with cryptographic certainty.
In an optimistic rollup, light clients have a different experience. They get some indication of the new rollup state very quickly (usually in the very next block), but they need to wait much longer (usually about a day) to be sure that their new view is correct. And, even in this case, clients only have "cryptoeconomic" certainty about the new state.
Proving Setup
In an optimistic rollup, the "proofs" checked by light clients are not (usually)
proofs at all. Instead, they are simple attestations. Attesters stake tokens on
claims like "the state of the rollup at height N is X", and anyone who
successfully challenges a claim gets to keep half of the staked tokens. (The
other half are burned to prevent an attester from lying about the state and then
challenging himself from another account and keeping his tokens). In exchange,
for their role in the process, attesters are rewarded with some portion of the
rollup's gas fees. This compensates attesters for the opportunity cost of
locking their capital.
This mechanism explains why light clients can know the state quickly with some confidence right away, but they take time to reach full certainty. Once they've seen an attestation to a state, clients know that either the state is correct, or the attester is going to lose some amount of capital. As time goes by and no one challenges the assertion, their confidence grows until it reaches (near) certainty. (The point at which clients are certain about the outcome is usually called the "finality period" or "finality delay".)
The previous generation of optimistic rollups (including Optimism and Arbitrum)
relies on running an on-chain bisection game over an execution trace to resolve
disputes about the rollup state. This requires $log_2(n)$ rounds of interaction,
where n is the length of the trace (i.e. a few hundred million). To handle the
possibility of congestion or censorship, rollups need to set the timeout period
of messages conservatively - which means that a dispute could take up to a week
to resolve.
In the Sovereign SDK, we resolve disputes by generating a zero-knowledge proof of the outcome of the disputed block. Since this only requires one round of interaction, we don't need the same challenge delay. However, we do need to account for the fact that proving is a heavy process. Generating a proof might take a few hours, and proving services might be experiencing congestion. To minimize the risk, we plan to set the finality period conservatively at first (about one day) and reduce it over time as we gain confidence.
Otherwise, the overall proving setup is quite similar to that of a zk-rollup. Just as in zk-rollups, proofs (and attestations) are posted onto the DA layer so that we have consensus about who to reward and who to slash. And, just like a zk-rollup, optimistic proofs/attestations are posted into a separate "namespace" on the DA layer (if possible) so that light clients can avoid downloading transaction data. The only other significant distinction between optimistic and zk rollups in Sovereign is that optimistic rollups use block-level proofs to resolve disputes instead of generating aggregate proofs which go all the way to genesis.
Conclusion
In the Sovereign SDK, we try to provide security, flexibility, and performance in that order.
As a contributor, it's your job to maintain that hierarchy. Security must always come first. And in blockchain, security is mostly about incentives. Especially in blockchain, you get what you incentivize. If your rollup under-prices some valuable resource, you'll get spam. If you under pay for some service, that service won't be provided reliably.
This is why incentive management is so deeply baked into the SDK. Every step - from sequencing to proving to execution to finality - needs to be carefully orchestrated to keep the incentives of the participants in balance.
Once the setup is secure, our next priority is enabling the broadest set of use cases. We try to provide maximum flexibility, and abstract as much functionality as possible into reusable components. You can read more about how we achieve flexibility at the level of Rust code in the abstractions chapter.
Finally, we optimize performance. This means eliminating redundant computation, carefully managing state access patterns, and considering the strengths and weaknesses of zero-knowledge proofs systems.
Happy hacking!
Main Abstractions
This document provides an overview of the major abstractions offered by the SDK.
- Rollup Interface (STF + DA service + DA verifier)
- sov-modules (
Runtime,Module, stf-blueprint w/ account abstraction, state abstractions)- sov-sequencer
- sov-db
- Rockbound
One of the most important principles in the Sovereign SDK is modularity. We believe strongly in separating rollups into their component parts and communicating through abstract interfaces. This allows us to iterate more quickly (since components are unaware of the implementation details of other components), and it also allows us to reuse components in contexts which are often quite different from the ones in which they were orginally designed.
In this chapter, we'll give a brief overview of the core abstractions of the Sovereign SDK
Native vs. ZK Execution
Perhaps the most fundamental abstraction in Sovereign is the separation between
"native" code execution (which computes a new rollup state) and zero-knowledge
verification of that state. Native execution is the experience you're used to.
In native execution, you have full access to networking, disk, etc. In native
mode, you typically trust data that you read from your own database, but not
data that comes over the network.
Zero-knowledge execution looks similar. You write normal-looking Rust code to do
CPU and memory operations - but under the hood, the environment is alien. In
zero-knowledge execution, disk and network operations are impossible. Instead,
all input is received from the (untrusted) machine generating the proof via a
special syscall. So if you make a call that looks like a network access, you
might not get a response from google.com. Instead, the prover will pick some
arbitrary bytes to give back to you. The bytes might correspond to an actual
response (i.e. if the prover is honest and made the network request for you) -
but they might also be specially crafted to deceive you. So, in zero-knowledge
mode, great care must be taken to avoid relying on unverified data from the
prover.
In the Sovereign SDK, we try to share code between the "native" full node
implementation and the zero-knowledge environment to the greatest extent
possible. This minimizes surface area for bugs. However, a full node necessarily
needs a lot of logic which is unnecessary (and undesirable) to execute in
zero-knowledge. In the SDK, such code is gated behind a cargo feature called
"native". This code includes RPC implementations, as well as logic to
pre-process some data into formats which are easier for the zero-knowledge code
to verify.
The Rollup Interface
If you squint hard enough, a zk-rollup is made of three separate components. There's an underlying blockchain ("Data Availability layer"), a set of transaction execution rules ("a State Transition Function") and a zero-knowledge proof system (a "ZKVM" for zero-knowledge virtual machine). In the abstract, it seems like it should be possible to take the same transaction processing logic (i.e. the EVM) and deploy it on top of many different DA layers. Similarly, you should be able to take the same execution logic and compile it down to several different proof systems - in the same way that you can take the same code an run it on Risc0 or SP1.
Unfortunately, separating these components can be tricky in practice. For example, the OP Stack relies on an Ethereum smart contract to enforce its censorship resistance guarantees - so, you can't easily take an OP stack rollup and deploy it on a non-EVM chain.
In the Sovereign SDK, flexibility is a primary design goal. So we take care to
codify this separation of concerns into the framework from the very beginning.
With Sovereign, it's possible to run any State Transition Function alongside
any Da Service on top of any (rust-compatible) proof system and get a
functional rollup. The rollup-interface crate is what makes this possible.
Every other crate in the SDK depends on it, because it defines the core
abstractions that are shared between all SDK rollups.
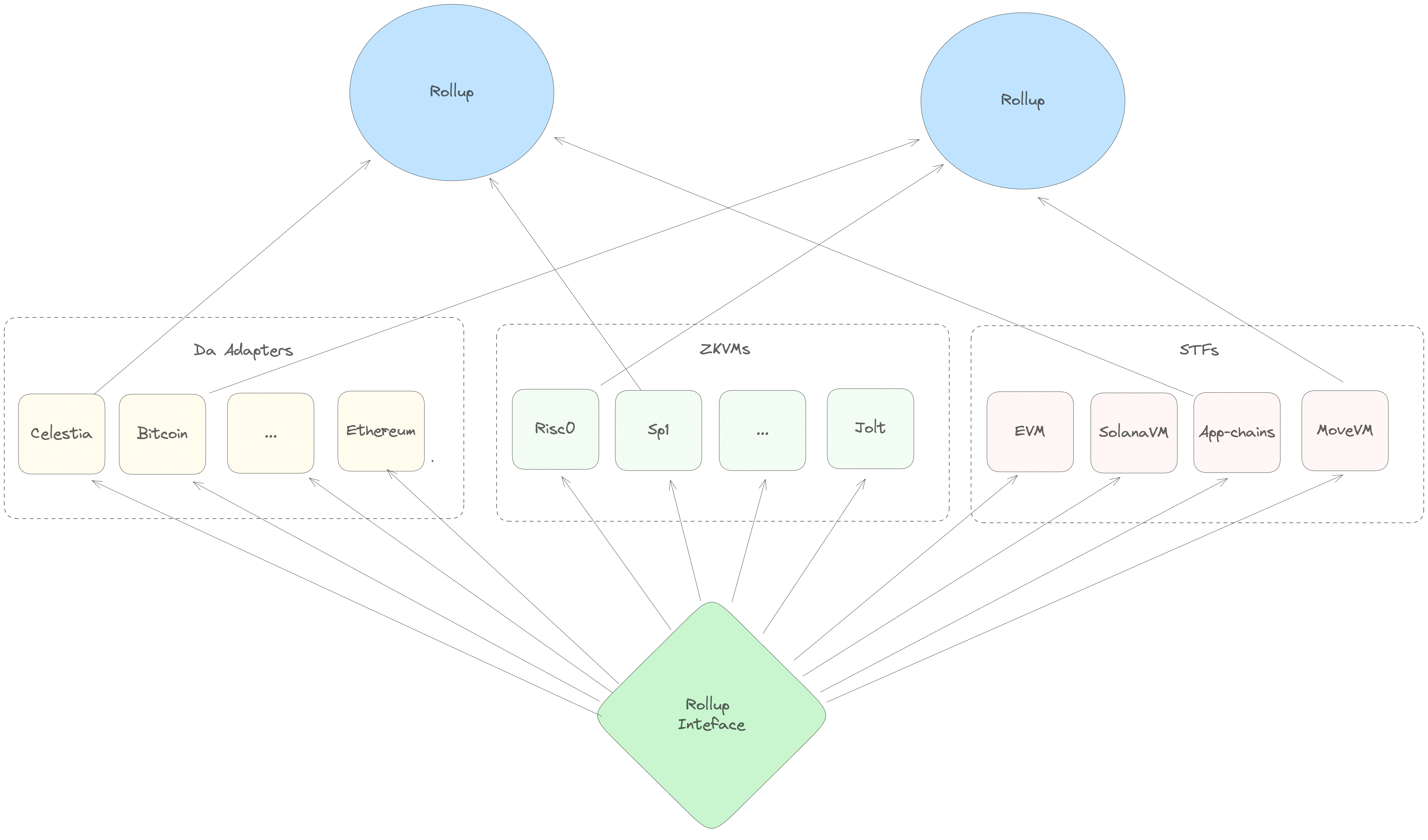
Inside of the rollup interface, the native vs zero-knowledge distinction
appears in numerous places. For example, the DA layer abstraction has two
components - a DaService, which runs as part of native full node execution
and provides methods for fetching data from the underlying blockchain; and
DaVerifier, which runs in zero-knowledge and verifies that the data being
executed matches the provided DA block header.
How it Works
Essentially, the Sovereign SDK is just a generic function that does this:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { fn run_rollup<Da: DaService, Zk: Zkvm, Stf: StateTransitionFunction>(self, da: Da, zkvm: Zk, business_logic: Stf) { loop { // Run some `native` code to get the data for execution let (block_data, block_header) = da.get_next_block(); let (input_state, input_state_root) = self.db.get_state(); // Run some zero-knowledge code to execute the block let proof = zkvm.prove(|| { // Check that the inputs match the provided commitments if !da.verify(block_data, block_header) || !input_state.verify(input_state_root) { panic!() }; // Make the data commitments part of the public proof output!(block_header.hash(), input_state_root) let output_state_root = business_logic.run(block_data, input_state); // Add the output root to the public proof output!(output_state_root) }); // Publish the proof onto the DA layer da.publish(proof); } } }
As you can see, most of the heavy lifting is done by the DA layer, the Zkvm
and the rollup's business logic. The full node implementation is basically just
glue holding these components together.
DA
As discussed above, the role of the DA layer is to order and publish data. To
integrate with the Sovereign SDK, a DA layer needs to provide implementations of
two core traits: DaService and DaVerifier.
DA Service
The DaService trait is usually just a thin wrapper around a DA layer's
standard RPC client. This trait provides standardized methods for fetching data,
generating merkle proofs, and publishing data. Because it interacts with the
network, correct execution of this trait is not provable in zero-knowledge.
Instead, the work of verifying of the data provided by the DaService is
offloaded to the DaVerifier trait. Since the DaService runs only in native
code, its implementation is less concerned about efficiency than zero-knowledge
code. It's also easier to patch, since updating the DaService does not
require any light clients or bridges to update.
The DaService is the only component of the SDK responsible for publishing and
fetching data. The SDK's node does not currently have a peer-to-peer network of
its own. This dramatically simplifies the full node and reduces bandwidth
requirements.
DA Verifier
The DaVerifier is the zero-knowledge-provable counterpart of the DaService.
It is responsible for checking that the (untrusted) private inputs to a proof
match the public commitment as efficiently as possible. It's common for the
DaVerifier to offload some work to the DaService (i.e. as computing extra
metadata) in order to reduce the amount of computation required by the
DaVerifier.
At the level of Rust code, we encode the relationship between the DaVerifier
and the DaService using a helper trait called DaSpec - which specifies the
types on which both interfaces operate.
Zero Knowledge Virtual Machine ("Zkvm")
The Zkvm traits make a zk-snark system (like Risc0 or Sp1) compatible with
the Sovereign SDK. Like the DA layer, we separate Zkvm traits into a
native and zk version, plus a shared helper.
The ZkvmHost trait describes how a native computer executes an elf file
(generated from Rust code) and generates a zero-knowledge proof. It also
describes how the native machine passes private inputs (the "witness") into
the execution.
The ZkvmGuest trait describes how a program running in zero-knowledge mode
accepts inputs from the host machine.
Finally, the ZkVerifier trait describes how a proof generated by the host is
verified. This trait is implemented by both the Host and the Guest, which is
how we represent that proofs must be verifiable natively and recursively (i.e.
inside another SNARK.)
State Transition
A StateTransitionFunction ("STF") is a trait which describes:
-
How to initialize a rollup's state at genesis
-
How to apply the data from the DA layer to generate a new state
In other words, the implementation of StateTransitionFunction is what defines
the rollup's "business logic".
In the Sovereign SDK, we define a generic full node which can run any STF. As long as your logic implements the interface, we should be able to run it.
However, implementing the business logic of a rollup is extremely complicated.
While it's relatively easy to roll your own implementation of the Da or Zkvm
traits, building a secure STF from scratch is a massive undertaking. It's so
complex, in fact, that we assume no one will ever do it - andthe vast majority
of the Sovereign SDK's code is devoted to providing a generic implementation of
an STF that developers can customize. (This STF is what we call the Sovereign
module system, or sov-modules).
So if no one is ever going to implement the StateTransitionFunction interface,
why bother maintaining it at all? One reason is for flexibility. Just because we
don't expect anyone to roll their own STF doesn't mean that they won't. But a
bigger motivation is to keep concerns separate. By hiding the implementation
details of the rollup behind the STF interface, we build a firm abstraction
barrier between it and the full node. This means that we're free to make
breaking changes on either side of the wall (either in the node, or in the STF)
without worrying about breaking the other component.
Sov Modules
Outside of the rollup interface, the most important abstraction is
sov-modules. sov-modules is a pre-built STF with pluggable... modules. It
does the heavy lifting of implementing a secure STF so that you can focus on the
core logic of your application.
The Runtime
At the heart of any sov-modules rollup is the Runtime:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { // An example runtime similar to the one used in our "standard" demo rollup pub struct Runtime<S: Spec> { /// The Bank module implements fungible tokens, which are needed to charge `gas` pub bank: sov_bank::Bank<S>, /// The Sequencer Registry module is where we track which addresses can send batches to the rollup pub sequencer_registry: sov_sequencer_registry::SequencerRegistry<S>, /// The Prover Incentives module is where we reward provers who do useful work pub prover_incentives: sov_prover_incentives::ProverIncentives<S>, /// The Accounts module implements identities on the rollup. All of the other modules rely on it /// to link cryptographic keys to logical accounts pub accounts: sov_accounts::Accounts<S>, /// The NFT module provides an implementation of a non-fungible token standard. It's totally optional. pub nft: sov_nft_module::NonFungibleToken<S>, #[cfg_attr(feature = "native", cli_skip)] /// The EVM module lets the rollup run Ethereum smart contracts. It's totally optional. pub evm: sov_evm::Evm<S, Da>, } }
At the highest level, a runtime is "just" a collection of all the modules which
are included in your rollup. Its job is to take Transactions and dispatch them
to the appropriate module for execution.
Pretty much all rollups built with the sov-modules include the bank, the
sequencer registry, and the accounts module in their Runtime. They also
usually include one of sov_prover_incentives (if they're a zk-rollup) or
sov_attester_incentives (if they're an Optimistic rollup).
You may also have noticed that the Runtime is generic over a Spec. This
Spec describe the core types (addresses, hashers, cryptography) used by the
rollup and the DA layer. Making your runtime generic over a Spec means that you
can easily change DA layers, or swap any of the core primitives of your rollup.
For example, a rollup can trivially switch from Ed25519 to secp256k1 for its
signature scheme by changing the implementation of its Spec trait.
Modules
"Modules" are the things that process transactions. For example, the Bank
module lets users transfer tokens to each other. And the EVM module implements
a full Ethereum Virtual Machine that can process any valid Ethereum transaction.
A Module is just a rust struct that implements two traits called Module
and ModuleInfo.
The Module trait
The Module trait is like a simplified version of the
StateTransitionFunction. It describes how to initialize the module at the
rollup's genesis, and how the module processes CallMessages received from
users (i.e. how it processes transactions)
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { pub trait Module { // -- Some associated type definitions are omitted here -- /// Module defined argument to the call method. type CallMessage: Debug; /// Genesis is called when a rollup is deployed and can be used to set initial state values in the module. fn genesis( &self, _config: &Self::Config, _working_set: &mut WorkingSet<Self::Spec>, ) -> Result<(), ModuleError>; /// Processes a transaction, updating the rollup state. fn call(&self, _message: Self::CallMessage, _context: &Context<Self::Spec>, _state: &mut impl TxState<S>, ) -> Result<CallResponse, ModuleError>; } }
You'll notice that the call function takes three arguments: an associated
CallMessage type, a Context, and a WorkingSet.
-
The
CallMessagetype is the deserialized content of the user's transaction - and the module can pick any type to be itsCallMessage. In most cases, modules use anenumwith one variant for each action a user might want to take. For example, theBank::CallMessagetype has variants for minting, transferring, and burning tokens. -
The
Contexttype is relatively straightforward. It simply contains the address of the sequencer, who published the transaction, the identity of the transaction's signer, and the current block height. -
The
TxStateis the most interesting of the three, but it needs a little bit of explanation. In the Sovereign SDK, the ruststructwhich implements aModuledoesn't actually contain any state. Rather than holding actual values, the module simply defines the structure of some items in state. All of the actual state of the rollup is stored in theStateobject, which is in-memory layer on top of the rollup's database (in native mode) or merkle tree (in zk mode). TheStateabstraction handles commit/revert semantics for you, as well as taking responsibility for caching, deduplication, and automatic witness generation/checking. It also provides utilities for charginggasand emittingevents.
The Accounts module provides a good example of a standard Module trait
implementation.
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { pub enum CallMessage<S: Spec> { /// Updates a public key for the corresponding Account. /// The sender must be in possession of the new key. UpdatePublicKey( /// The new public key <S::CryptoSpec as CryptoSpec>::PublicKey, /// A valid signature from the new public key <S::CryptoSpec as CryptoSpec>::Signature, ), } impl<S: Spec> sov_modules_api::Module for Accounts<S> { // -- Some items ommitted here -- fn call( &self, msg: Self::CallMessage, context: &Context<S>, working_set: &mut WorkingSet<S>, ) -> Result<sov_modules_api::CallResponse, Error> { match msg { call::CallMessage::UpdatePublicKey(new_pub_key, sig) => { // Find the account of the sender let pub_key = self.public_keys.get(context.sender(), working_set)?; let account = self.accounts.get(&pub_key, working_set); // Update the public key self.accounts.set(&new_pub_key, &account, working_set); self.public_keys .set(context.sender(), &new_pub_key, working_set); Ok(Default::default()) } } } } }
The ModuleInfo trait
The ModuleInfo trait describes how the module interacts with the broader
module system. Each module has a unique ID and stores its state under a unique
prefix of the global key-value store provided by sov-modules
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { pub trait ModuleInfo { /// Returns id of the module. fn id(&self) -> &ModuleId; /// Returns the prefix where module state is stored. fn prefix(&self) -> ModulePrefix; /// Returns addresses of all the other modules this module is dependent on fn dependencies(&self) -> Vec<&ModuleId>; } }
Unlike the Module trait, its incredibly rare for developers to implement
ModuleInfo by hand. Instead, it's strongly recommended to derive the
ModuleInfo using our handy macro. A typical usage looks like this:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { #[derive(ModuleInfo, Clone)] pub struct Bank<S: sov_modules_api::Spec> { /// The id of the sov-bank module. #[id] pub(crate) id: ModuleId, /// The gas configuration of the sov-bank module. #[gas] pub(crate) gas: BankGasConfig<S::Gas>, /// A mapping of [`TokenId`]s to tokens in the sov-bank. #[state] pub(crate) tokens: sov_modules_api::StateMap<TokenId, Token<S>>, } }
This code automatically generates a unique ID for the bank module and stores it
in the field of the module called id. It also initializes the StateMap
"tokens" so that any keys stored in the map will be prefixed the with module's
prefix. This prevents collisions in case a different module also declares a
StateMap where the keys are TokenIds.
Module State
The Sovereign SDK provides three core abstractions for managing module state. A
StateMap<K, V> maps arbitrary keys of type K to arbitrary values of type
V. A StateValue<V> stores a value of type V. And a StateVec<V> store an
arbitrary length vector of type V. All three types require their arguments to
be serializable, since the values are stored in a merkle tree under the hood.
All three abstractions support changing the underlying encoding scheme but
default to Borsh if no alternative is specified. To override the default,
simply add an extra type parameter which implements the StateCodec trait. (i.e
you might write StateValue<Da::BlockHeader, BcsCodec> to use the Bcs
serialization scheme for block headers, since your library for DA layer types
might only support serde-compatible serializers).
All state values are accessed through TxState. For example, you always write
my_state_value.get(&mut state) to fetch a value. It's also important to
remember that modifying a value that you read from state doesn't have any effect
unless you call my_value.set(new, &mut working_set).
Merkle Tree Layout
sov-modules currently uses a generic
Jellyfish Merkle Tree for its
authenticated key-value store. (Generic because it can be configured to use any
32-byte hash function). In the near future, this JMT will be replaced with the
Nearly Optimal Merkle Tree
that is currently under development.
In the current implementation, the SDK implements storage by generating a unique
(human-readable) key for each StateValue, using the hash of that key as a path
in the merkle tree. For StateMaps, the serialization of the key is appended to
that path. And for StateVecs, the index of the value is appended to the path.
For example, consider the following module:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { // Suppose we're in the file my_crate/lib.rs #[derive(ModuleInfo, Clone)] pub struct Example<S: sov_modules_api::Spec> { #[id] pub(crate) id: ModuleId, #[state] pub(crate) some_value: sov_modules_api::StateValue<u8>, #[state] pub(crate) some_vec: sov_modules_api::StateVec<u64>, #[state] pub(crate) some_map: sov_modules_api::StateMap<String, String>, } }
The value of some_value would be stored at the path
hash(b"my_crate/Example/some_value"). The value of the key "hello" in
some_map would be stored at hash(b"my_crate/Example/some_map/⍰hello") (where
⍰hello represents the borsh encoding of the string "hello") etc.
However, this layout may change in future to provide better locality. For more details... ask Preston, I guess.
Exotic State Variants
In addition to the standard state store, we support two other kinds of state:
KernelStateValues or (maps/vecs) act identically to regular StateValues, but
they're stored in a separate merkle tree which is more tightly access
controlled. This mechanism allows the rollup to store data that is inaccessible
during transaction execution, which is necessary to enable soft-confirmations
without sacrificing censorship resistance. For more details, see the section on
soft-confirmations in the transaction lifecycle
documentation. The global "state root" returned by the sov-modules from the
StateTransitionFunction implementation is the hash of the kernel state root
with the regular state root. We do our best to hide this detail from users of
the SDK, though. Merkle proofs are automatically generated against the global
root, so users don't need to worry about which state trie there values are in.
AccessoryStateValue or (map/vec) types are similar to Kernel types except
that their values are not readable from inside the state transition function
at all. Under the hood, these value are stored in the rollup's database but not
in either merkle tree. This is useful for creating data that will be served via
RPC but never accessed again during execution - for example, the transaction
receipts from an Ethereum block.
The STF Blueprint
The last key component of a sov-modules rollup is the stf-blueprint. This
"blueprint" provides a generic implementation of a StateTransitionFunction in
terms of a Runtime (described above) and a Kernel (which provides
security-critical functionality like censorship resistance in a way that's
isolated from the transaction execution logic).
The STF blueprint implements the following high-level workflow:
- Take all of the new data
Blobs read from the DA layer and send them to theKernel. TheKernelwill return a list of deserializedBatches of transactions as well as the currentgasprice. (A "Batch" is a "Blob" sent by a registered sequencer that has been succesfully deserialized into a list ofTransactions)
- Note that the list of
Batches returned by theKerneldoes not necessarily correspond exactly to the incomingBlobs. TheKernelmight decide to ignore some Blobs, or to store some in its internal state for "deferred" execution. It might also add someBatches saved from a previous slot.
-
Run the
begin_slothook, allowing modules to execute any initialization logic -
For each batch initialize the sequencer reward to zero and run the
begin_batchhook. Apply the transactions, rewarding or penalizing the sequencer as appropriate. Finally, run theend_batchhook -
Run the
end_slothook to allow modules to execute any final logic. -
Compute the state change set and state root based on the transactions that were executed.
-
Execute the
finalizehook, which allows modules to compute any summary information from the change set and make it available via RPC.
For more details on the process of applying individual transactions, see the transaction lifecycle document.
Sequencer Registration via Forced Inclusion
Forced inclusion is a strategic mechanism in rollups designed to circumvent sequencers that censor user transactions. It allows users to directly submit transaction batches to the Data Availability Layer instead of going through a sequencer.
The Sovereign SDK supports this feature under specific conditions and guidelines. Crucially, only "Register Sequencer" transactions are accepted for forced inclusion; all other types will be ignored. For more details, see the Rules section.
Usage
The Sovereign SDK limits the number of batches from unregistered sequencers processed per rollup slot. This measure limits the use of this mechanism as a denial-of-service (DOS) attack vector.
Process for Forced Registration
- Create a batch containing a valid "Register Sequencer" transaction.
- Submit the batch to the Data Availability layer.
- Rollup nodes collect and execute the transaction.
- If the transaction complies with all rules, the user is registered as a sequencer and can submit regular transaction batches.
Rules
To ensure forced inclusion requests are processed correctly, the following rules apply:
- Transaction Limit: Only the first transaction in each batch is taken into account. Any additional transactions will be discarded.
- Transaction Type: The transaction must be a "Register Sequencer" transaction.
- Transaction Construction: The transaction must be properly formatted and comply with standard transaction rules.
- Financial Requirements: Users must have enough funds to cover:
- Pre-execution checks (including signature validation, deserialization and transaction type checks).
- Transaction execution costs.
- A bond required for sequencer registration.
Gas Specification
This document contains a detailed specification of the way gas is handled within
Sovereign's SDK. We use <., .> to denote the scalar product of two
multidimensional quantities.
Definition
Gas is an ubiquitous concept in the blockchain space. It is a measure of the computational effort required to perform an operation as part of a transaction execution context. This is used to prevent the network from getting spammed by regulating the use of computational resources by each participant in the network.
High level overview
We have drawn a lot of inspiration from the Ethereum gas model in our gas mechanism design. Given that Ethereum's gas is well understood and widely used in the crypto industry, we believe that this will help users onboard more easily while providing strong security guarantees out-of-the box. We have deliberately chosen to tweak some concepts that were ill-suited to the rollups built using Sovereing's SDK. In particular, sorted decreasing order of importance:
- We are using multidimensional gas units and prices.
- We plan to using a dynamic gas target. Otherwise, the rollups built with Sovereign's SDK follow the EIP-1559 specification by default.
- Rollup transactions specify a
max_fee,max_priority_fee_bips, and optional gas limitgas_limit. The semantics of these quantities roughtly match their definition in the EIP-1559 specification. - Transaction rewards are decomposed into
base_feeandpriority_fee. Thebase_feeis only partially burnt by default, the remaining amount is used to reward provers/attesters. Thepriority_feeis used to reward the block sequencers. - We are charging gas for every storage access within the module system by default.
- Customers of the SDK will have access to wrappers that allow to charge gas for hash computation and signature checks.
A design for multidimensional gas
Sovereign SDK's rollups use multidimensional gas units and prices. For example, this allows developers to take into account the differences between native and zero-knowledge computational costs for the same operation. Indeed:
- Hashing is orders of magnitude more expensive when performed inside a
zero-knowledge circuit. The cost of proving the correct computation of two
different Hash may also vary much more than the cost of computing the hash
itself (
PoseidonorMiMcvsSha2). - Accessing a storage cell for the first time is much more expensive in
zkmode than innativemode. But hot storage accesses are practically free in zero-knowledge.
In the Sovereign SDK, we currently meter consumption in two dimensions - compute and memory.
We have chosen to follow the multi-dimensional EIP-1559 design for the gas pricing adjustment formulas. In essence:
- We are performing the gas price updates for each dimension separately. In other words, each dimension follows a separate uni-dimensional EIP-1559 gas price adjustment formula.
- The gas price adjustment formula uses a
gas_targetreference, which is a uni-dimensional gas unit that is compared to the gas consumedgas_used. Thegas_priceis then adjusted to regulate the gas throughtput to get as close as possible to thegas_target. We have the following invariant:0 <= gas_used_slot <= 2 * gas_target. - Contrarily to Ethereum, we are planning to design a dynamic
gas_target. The value of thegas_targetwill vary slowly to follow the evolution of the rollup metrics we have described above. That way, Sovereign rollups can account for major technological improvements in computation (such as zk-proof generation throughtput), or storage cost. - Every transaction has to specify a scalar
max_feewhich is the maximum amount of gas tokens that can be used to execute a given transaction. Similarly, users have to specify amax_priority_fee_per_gasexpressed in basis points which can be used to reward the transaction sequencer. - The final sequencer reward is:
seq_reward = min(max_fee - <base_fee, gas_price>, max_priority_fee_per_gas * <base_fee, gas_price>). - Users can provide an optional
gas_limitfield which is a maximum amount of gas to be used for the transaction. This quantity is converted to a uni-dimensionalremaining_fundsquantity by taking the scalar product with the currentgas_price. - If users provide the
gas_limit, the rollup checks that<gas_limit, current_gas_price> <= max_fee(ie, the scalar product with the currentgas_price). If the check fails, the associated transaction is not executed and the rollup raises aReserveGasErrorReason::CurrentGasPriceTooHigherror.
Charging gas for state accesses.
State accessors such as the WorkingSet or the PreExecWorkingSet charge some
gas whenever state is modified. If these accessors run out of gas, they return a
StateAccessorError and the execution gets reverted (or the sequencer is
penalized). Some state accessors - like StateCheckpoint, the TxScratchpad or
the ApiStateAccessor - don't charge for gas for state accesses. In that case,
the access methods return a Result<T, Infallible> type which can be unwrapped
safely using unwrap_infallible.
For now, we are enforcing simple cached access patterns - we are refunding some gas if the value that is accessed/modified is hot (ie has been already accessed and is cached).
Gas rewards.
The gas consumed during transaction execution is used to reward both
provers/attesters and block sequencers. The base_fee, ie the total amount of
gas consumed by the transaction execution is partially burnt (the amount to burn
is specified by the PERCENT_BASE_FEE_TO_BURN constant), and the remaining
portion is locked in a reward pool to be redeemed by provers/attesters. The
priority_fee is also partially burnt and used to reward block sequencers.
Additional data structures that can be used to charge gas.
We have a couple of additional data structures that can be used to charge gas. These are:
MeteredHasher: a wrapper structure that can be used to charge gas for hash computation.MeteredSignature: a wrapper structure that can be used to charge gas for signature checks.MeteredBorshDeserialize: a supertrait that can be used to charge gas for structures implementingBorshDeserialize.
Structure of the implementation
The core of the gas implementation is located within the sov-modules-api crate
in the following modules/files:
module-system/sov-modules-api/src/common/gas.rs: contains the implementation of theGasandGasMetertraits. These are the core interfaces that are consumed by the API. TheGastrait defines the way users can interact with multidimensional gas units. TheGasMeteris the interface implemented by every data structure that contains or consumes gas (such as theWorkingSetwhich contains aTxGasMeter, or thePreExecWorkingSetthat may contain aSequencerStakeMeter).module-system/sov-modules-api/src/common/hash.rs: contains the implementation of theMeteredHasherwhich is a wrapper structure that can be used to charge gas for hash computation.module-system/sov-modules-api/src/transaction.rs: contains the representation of the transaction type that is used within the SDK. These structures contain themax_fee,max_priority_fee_bipsandgas_limitfields that represent the maximum amount of gas tokens to use for the transaction, the maximum priority fee to pay the sequencer (in basis points), and an optionnal multidimensional gas limit (ie the maximum amount of gas to be consumed for this transaction).
Outside of the sov-modules-api, within the module system:
module-system/module-implementations/sov-chain-state/src/gas.rs:compute_base_fee_per_gascontains the implementation of the gas price update which follows our modified version of theEIP-1559. The gas price is updated within theChainState's module lifecycle hooks (ChainState::begin_slot_hookupdates the gas price,ChainState::end_slot_hookupdates the gas consumed by the transaction).module-system/module-implementations/sov-sequencer-registry/src/capabilities.rs: contains the implementationn of theSequencerStakeMeterwhich is the data structure used to meter the sequencer stake before the transaction's execution starts.
